Are you shivering at the thought of your EV's range plummeting in winter? The secret to staying warm and maximizing efficiency lies within the often-overlooked heat pump! Discover how EV heat pumps work to improve efficiency in cold weather, extending your driving range and keeping you cozy. This article will explore the technology behind these systems, their benefits for EV owners, practical usage tips, and common troubleshooting steps.
All About EV Heat Pumps: Improving Efficiency in Cold Weather
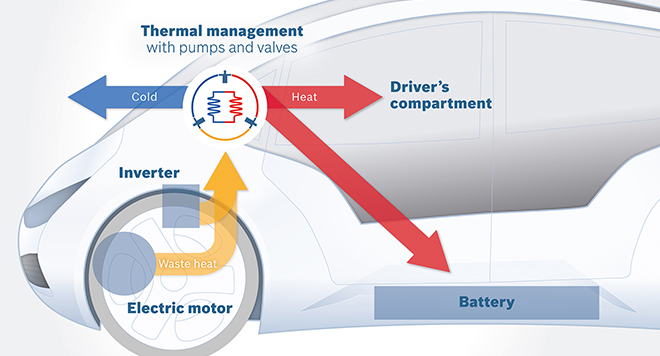
Electric vehicles are fantastic, but cold weather can significantly impact their range. Traditional heating systems in cars rely on resistive heaters, essentially giant electric space heaters, which draw a considerable amount of power. That's where heat pumps come in. EV heat pumps offer a much more efficient way to heat the cabin, making winter driving less of a range anxiety nightmare. EV heat pumps work by moving heat, rather than generating it, drastically improving efficiency in cold weather.
Think of it like this: a refrigerator doesn't create cold; it moves heat from inside the fridge to the outside. A heat pump does something similar. It extracts heat from the outside air (even when it's cold!) and transfers it inside the car. This process uses significantly less energy than a resistive heater, allowing for a noticeable improvement in range during colder months. Understanding how EV heat pumps work is crucial for maximizing the benefits of your electric vehicle.
The idea of using heat pumps in vehicles isn't new, but their application in EVs has become more prevalent as manufacturers strive to improve efficiency and range. Early adopters faced challenges with performance in very low temperatures, but advancements in technology, such as improved refrigerants and more sophisticated control systems, have significantly enhanced their effectiveness. This evolution of EV heat pumps work towards better thermal management is a constant area of research and development.
One key feature that differentiates EV heat pumps from other heating systems is their ability to provide both heating and cooling. In the summer, the heat pump reverses the process, removing heat from the cabin and dissipating it outside, acting as an air conditioner. Another differentiating factor is the coefficient of performance (COP). A resistive heater has a COP of 1 (for every unit of energy consumed, it produces one unit of heat). A heat pump can have a COP of 2 or even higher, meaning it produces two or more units of heat for every unit of energy consumed.
"Heat pumps are a game-changer for EV efficiency in cold climates," says Dr. Emily Carter, a leading researcher in electric vehicle thermal management. "They offer a significant improvement in range compared to traditional resistive heaters, making EVs a more practical option for drivers in colder regions." Many early adopters and experienced EV drivers echo this sentiment, praising the extended range and consistent heating provided by heat pumps.
Benefits of EV Heat Pumps: Improving Efficiency in Cold Weather for Users
The most significant benefit of EV heat pumps is the increased efficiency, particularly in cold weather. This translates directly into extended driving range, reducing range anxiety and making long winter trips more feasible. Imagine being able to drive significantly further on a single charge, even when the temperature dips below freezing – that's the power of a heat pump.
Beyond range extension, heat pumps provide more consistent and comfortable cabin heating. Unlike resistive heaters that can feel uneven, heat pumps distribute heat more evenly throughout the vehicle. This results in a more pleasant driving experience for both the driver and passengers.
Let's consider a real-life example. Two identical EVs, one equipped with a heat pump and the other with a resistive heater, are driven on the same route in -5°C (23°F) weather. The EV with the resistive heater sees its range reduced by approximately 40%, while the EV with the heat pump experiences a range reduction of only 20-25%. This significant difference demonstrates the tangible benefits of using a heat pump.
Compared to resistive heaters, heat pumps are also generally more energy-efficient overall, even in milder weather. While resistive heaters convert electricity directly into heat, heat pumpsmoveheat, requiring less energy to achieve the same level of warmth. Some advanced systems even incorporate waste heat recovery to further improve efficiency.
Data from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) supports these claims. NREL studies have shown that heat pumps can improve EV efficiency by up to 60% in cold weather compared to resistive heaters. This research provides compelling evidence of the significant benefits of heat pump technology.
How to Use EV Heat Pumps: Improving Efficiency in Cold Weather
While you can't exactly "use" a heat pump in the same way you use a navigation system, understanding how it operates and how to optimize its performance can significantly impact your EV's efficiency.
1. Preconditioning Your Vehicle
One of the best ways to maximize the efficiency of your heat pump is to precondition your vehicle while it's still plugged in. Most EVs allow you to remotely activate the heating system through a mobile app. This preheats the cabin using grid power, reducing the strain on the battery and the heat pump when you start driving. Consider preconditioning your EV 15-30 minutes before departing, especially on extremely cold days.
2. Setting the Temperature Wisely
Avoid setting the temperature too high. Heat pumps are most efficient when maintaining a moderate temperature. Instead of cranking the heat to the maximum, try setting it to a comfortable level (e.g., 20-22°C or 68-72°F) and letting the system maintain that temperature. Each degree you increase the temperature requires more energy from the system.
3. Utilizing Seat and Steering Wheel Heaters
Leverage the efficiency of seat and steering wheel heaters. These localized heating elements use less energy than heating the entire cabin. Consider using them in conjunction with the heat pump to stay comfortable while minimizing energy consumption. Many EVs have settings to automatically activate these features in cold weather.
4. Understanding Recirculation Mode
Use the recirculation mode wisely. While recirculating air within the cabin helps to maintain a consistent temperature and reduces the load on the heat pump, it can also lead to window fogging. Use it sparingly and switch to fresh air mode periodically to prevent condensation.
Tips Before Using EV Heat Pumps: Improving Efficiency in Cold Weather
Before relying on your EV's heat pump in cold weather, there are a few things to keep in mind.
Ensure your vehicle's software is up to date. Manufacturers often release software updates that improve the performance and efficiency of heat pump systems. Check your vehicle's settings or contact your dealer to ensure you have the latest software version installed.
Be aware that extreme cold can still impact heat pump performance. While heat pumps are much more efficient than resistive heaters, their effectiveness can decrease in very low temperatures (below -15°C or 5°F). In these conditions, the heat pump may need to work harder, resulting in a slight reduction in range.
Ignoring these tips can lead to decreased range and potentially uncomfortable driving conditions. Properly maintaining your vehicle and understanding its systems are crucial for optimal performance.
Common Issues and Solutions Related to EV Heat Pumps: Improving Efficiency in Cold Weather
While heat pumps are generally reliable, some common issues can arise.
One potential problem is reduced heating performance. This could be due to a low refrigerant level, a faulty compressor, or a clogged filter. Schedule a service appointment with your EV dealer to diagnose and repair any issues with the heat pump system.
Another issue is unusual noises. Grinding, squealing, or rattling noises could indicate a mechanical problem with the heat pump. Again, professional diagnosis and repair are recommended.
In some cases, the heat pump may switch to resistive heating in extremely cold temperatures. This is a normal operating procedure designed to ensure adequate heating in extreme conditions.
Conclusion
EV heat pumps are a critical technology for improving efficiency in cold weather and extending the range of electric vehicles. By understanding how they work, optimizing their usage, and addressing potential issues proactively, you can maximize their benefits and enjoy a more comfortable and efficient driving experience. Embracing the advancements in EV technology, like heat pumps, makes electric vehicles a more practical and appealing choice for drivers in all climates. Make sure to use preconditioning features, regulate temperature effectively, and maintain your vehicle to get the most out of your EV heat pump and ensure a comfortable and efficient ride, even when the temperature drops.